Radiation Dose-Reduction System Market Size, Share, Growth & Trends 2034

Radiation Dose-Reduction System Market By Products & Services (Standalone Solutions, Integrated Solutions, Services), By Modality (Computed Tomography, Fluoroscopy and Interventional Imaging, Nuclear Medicine, Radiography and Mammography), By End User( Ambulatory Care Settings, Hospital, Other), and By Region - Global and Regional Industry Overview, Market Intelligence, Comprehensive Analysis, Historical Data and Forecasts 2025 - 2034
| Market Size in 2024 | Market Forecast in 2034 | CAGR (in %) | Base Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| USD 2.48 Billion | USD 8.55 Billion | 13.2% | 2024 |
Radiation Dose-Reduction System Market Size
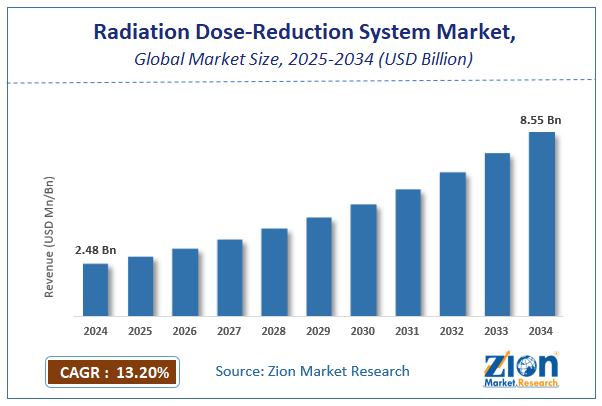
The global radiation dose-reduction system market size was worth around USD 2.48 Billion in 2024 and is predicted to grow to around USD 8.55 Billion by 2034 with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of roughly 13.2% between 2025 and 2034. The report analyzes the global radiation dose-reduction system market's drivers, restraints/challenges, and the effect they have on the demands during the projection period. In addition, the report explores emerging opportunities in the radiation dose-reduction system industry. The report analyzes the Radiation Dose-Reduction System market’s drivers, restraints/challenges, and the effect they have on the demands during the projection period. In addition, the report explores emerging opportunities in the Radiation Dose-Reduction System market.
Radiation Dose-Reduction System Market: Overview
A radiation dose-reduction system is a device that adjusts various factors, such as the distance between an examination table and the tube head, to help lower the amount of x-ray irradiated. The primary goal of this technology's development is to improve patient safety while performing medical examinations. Radiology departments are implementing many strategies for decreasing the intensity of X-Ray rays on the human body as technology advances.
Growing geriatric population, rising prevalence of chronic diseases such as cancer and cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) across the globe, rising awareness of early disease diagnosis and treatment, and increasing number of medical imaging and radiation procedures are all driving the global radiation dose management market revenue growth.Other major factors driving the global market revenue growth include the rapid adoption of technologically advanced medical imaging modalities such as computer tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and positron emission tomography (PET), rising concerns about sensitivity to radiation exposure, adverse health effects of radiation exposure in several cases, and the growing need for better radiation dose control and management.
Medical imaging helps physicians to view different internal areas of the human body and assist them in obtaining vital clinical information. Noninvasive diagnosis is assisted through imaging procedures that allow disease monitoring and support surgical and medical treatment planning. For several diseases, early detection is essential to reduce morbidity and opt for better treatment options. However, like all medical procedures, medical imaging, and nuclear medicine imaging exams present both benefits and risks. Medical imaging procedures use ionization radiations, which expose patients to high-intensity radiation doses, which might increase a person’s risk of developing cancer. Thus, managing the risks associated with radiation doses through medical imaging procedures have become a necessity for safe healthcare.
Key Insights
- As per the analysis shared by our research analyst, the global radiation dose-reduction system market is estimated to grow annually at a CAGR of around 13.2% over the forecast period (2025-2034).
- Regarding revenue, the global radiation dose-reduction system market size was valued at around USD 2.48 Billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 8.55 Billion by 2034.
- The radiation dose-reduction system market is projected to grow at a significant rate due to rising concerns over radiation exposure, stringent regulatory guidelines, advancements in imaging technologies, and increasing demand for safer diagnostic procedures in healthcare.
- Based on Products & Services, the Standalone Solutions segment is expected to lead the global market.
- On the basis of Modality, the Computed Tomography segment is growing at a high rate and will continue to dominate the global market.
- Based on the End User, the Ambulatory Care Settings segment is projected to swipe the largest market share.
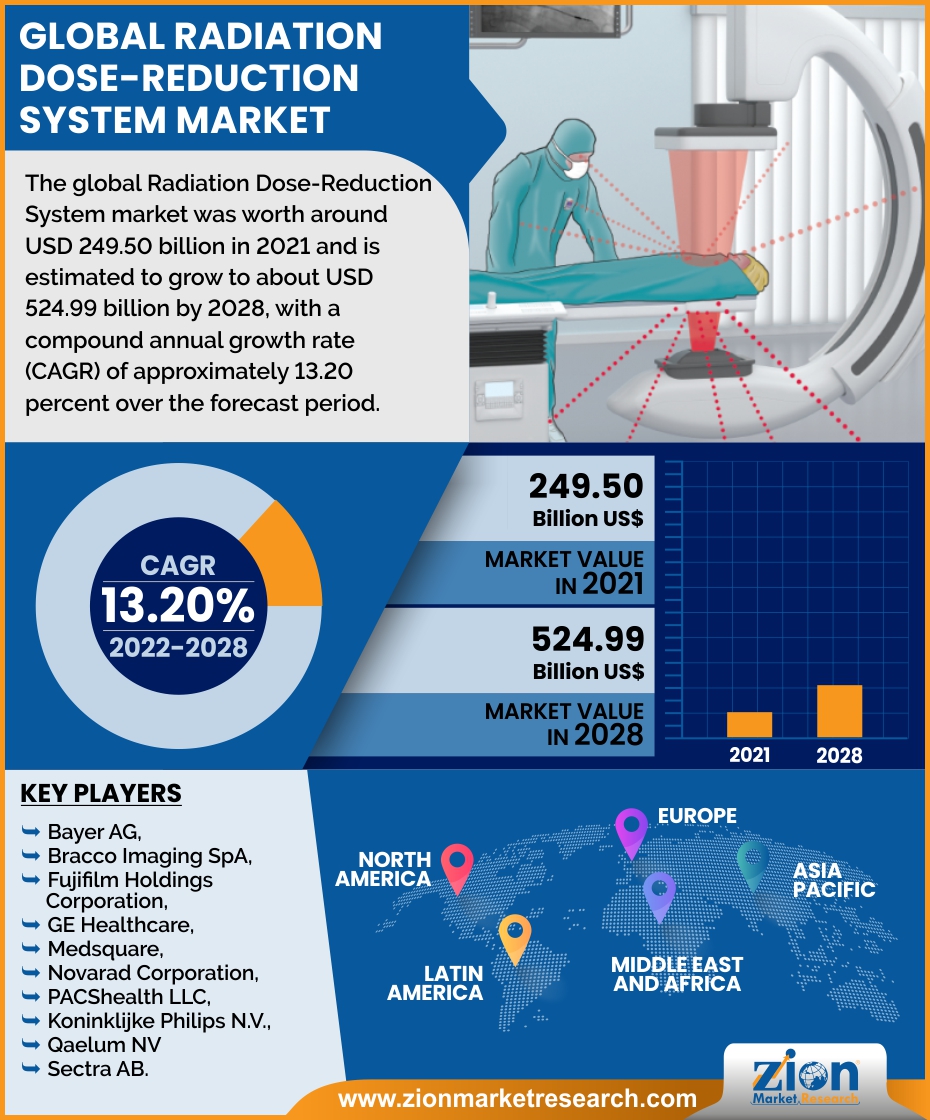
- Based on region, North America is predicted to dominate the global market during the forecast period.
Radiation Dose-Reduction System Market: Growth Drivers
Growing concerns over radiation exposure to drive global market growth
Radiation exposure to patients has increased dramatically over the previous two decades. This is due to an increase in the radiation doses used in radiological procedures such as CT, fluoroscopy, and interventional imaging techniques, as well as an increase in the utilization of these treatments. For obese individuals, greater tube currents are employed in diagnostic imaging modalities to increase image quality. Obese people are at a higher risk of radiation overexposure as a result of this. Previously, dose management was not a big concern for the medical community, which was more concerned with image quality (with overexposure providing better images). As a result, the radiation dosages employed in procedures began to rise steadily. Patients were more likely to be exposed to too much radiation as a result of this.
Radiation Dose-Reduction System Market: Restraints
High service & treatment charges in Radiation Dose-Reduction Systems to hamper the market growth
The charges connected with Radiation Dose-Reduction Systems are a major factor limiting their growth. This is mostly due to high operational costs and service charges. Technology is always improving, which has an impact on the cost of treatment at Radiation Dose-Reduction Systems because they must keep up with the latest equipment and technologies in order to maintain a competitive advantage.
Radiation Dose-Reduction System Market: Opportunities
Growing focus on interventional radiology and nuclear medicine to bring growth opportunities for global market
Because of their great imaging efficiency, interventional radiology and nuclear medicine treatments are becoming increasingly popular around the world. Patients get a very high dosage of radiation during these treatments, which, combined with the prolonged duration of these procedures, can raise the risk of cancer in those who undertake them. The Society of Nuclear Medicine estimates that over 20 million nuclear medicine operations are performed in the United States each year. According to the World Nuclear Association, radioisotopes are used in medicine in more than 10,000 hospitals around the world, with 90 percent of treatments employing radioisotopes being diagnostic. As a result, numerous market participants, such as Bayer Healthcare and Sectra Medical Systems, are delivering dose management software specifically for RDM in interventional imaging and nuclear medicine to meet the needs of end-users. Despite the fact that CT applications account for a big portion of the radiation dose control industry, interventional radiology and nuclear medicine applications are likely to rise significantly in the next five years..
Radiation Dose-Reduction System Market: Challenges
Lack of benchmarking for dose optimization across the globe may give rise to challenges for its growth
Government-defined guidelines for radiation dose benchmarking across all radiology procedures do not exist. Dose management software cannot be completely leveraged to achieve dose reduction due to the lack of established practises. The American College of Radiology has been attempting to develop national guidelines for CT treatments through DIR since 2011, however benchmarking for all imaging modalities must be done globally. On a global scale, consistent protocols are required for all sorts of examinations, imaging modalities, and patients of all sizes and ages. Individual practises would be able to monitor dose indices and compare standard dose reduction measures followed by similar healthcare provider facilities at the regional, state, national, and international levels if thorough benchmarking criteria and established protocols were available.
Global Radiation Dose-Reduction System Market: Segmentation
The global Radiation Dose-Reduction System market is segregated based on product & services, modality, end user, and region.
By products & services, the market is classified into standalone solutions, integrated solutions and services. During the projection period, the standalone solutions segment is expected to develop at the fastest rate. The growing adoption of radiation dose control solutions by healthcare providers as a result of tightening ionising radiation laws around the world is a major driver driving this segment's growth.
By modality, the market is divided into computed tomography, fluoroscopy and interventional imaging, nuclear medicine and radiography and mammography. In the modality segment, computed tomography is expected to grow at the fastest rate. Radiation exposure in patients undergoing computed tomography (CT) has increased, resulting in burns and radiation poisoning. Manufacturers are including technology for precise dose prediction for a CT process due to high dosage exposures while conducting CT scans. The risk of radiation exposure to patients is reduced with new CT equipment that includes dose reduction hardware and software. Bayer's Radimetric Enterprise Platform, for example, automates dose documentation with Certegra and the Medrad Stellant CT injectable device. Because it captures the image of the entire brain with a single 640-slice rotation, the Canon Medical Systems Aquilion One/Genesis Edition CT can eliminate the necessity for multimodality studies.
Radiation Dose-Reduction System Market: Report Scope
| Report Attributes | Report Details |
|---|---|
| Report Name | Radiation Dose-Reduction System Market |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 2.48 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2034 | USD 8.55 Billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 13.2% |
| Number of Pages | 195 |
| Key Companies Covered | Bayer AG, Bracco Imaging SpA,Fujifilm Holdings Corporation,GE Healthcare, Medsquare, Novarad Corporation, PACShealth LLC, Koninklijke Philips N.V., Qaelum NV and Sectra AB, and others. |
| Segments Covered | By Products & Services, By Modality, By End User, and By Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), Latin America, The Middle East and Africa (MEA) |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Historical Year | 2020 to 2023 |
| Forecast Year | 2025 - 2034 |
| Customization Scope | Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. Request For Customization |
Radiation Dose-Reduction System Market: Regional Landscape
North America is the leading region in this market. According to a survey published by Harvard Medical School, more than 80 million CT scans are performed in the United States each year. CT angiography, colonography, and dual-energy and perfusion CT are examples of scanning procedures that have changed diagnosis and therapy. However, due to the hazards linked with ionising radiation, there is growing worry about high-dose radiation exposure. As a result, radiology departments are performing CT scans with minimal doses. Many research centres and hospitals are employing modern state-of-the-art CT equipment that are coupled with software and ERP systems to provide accurate radiation dose estimates that can be compared to reference standards. The average dosage is calculated using the past CT examination doses by the dose tracking software.The US radiation dose management market is likely to grow at a healthy rate throughout the forecast period due to the aforementioned factors.
Radiation Dose-Reduction System Market: Competitive Landscape
The report provides a company market share analysis to give a broader overview of the key market players. In addition, the report also covers key strategic developments of the market, including acquisitions & mergers, new product launches, agreements, partnerships, collaborations & joint ventures, research & development, and regional expansion of major participants involved in the radiation dose-reduction system market on a global and regional basis.
Some of the main competitors dominating the global Radiation Dose-Reduction System market include
- Bayer AG
- Bracco Imaging SpA,Fujifilm Holdings Corporation,GE Healthcare
- Medsquare
- Novarad Corporation
- PACShealth LLC
- Koninklijke Philips N.V.
- Qaelum NV and Sectra AB.
Global Radiation Dose-Reduction System market is segmented as follows:
By Products & Services
- Standalone Solutions
- Integrated Solutions
- Services
By Modality
- Computed Tomography
- Fluoroscopy and Interventional Imaging
- Nuclear Medicine
- Radiography and Mammography
By End User
- Ambulatory Care Settings
- Hospital
- Other End Users
By Region
- North America
- The U.S.
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Germany
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- Australia
- South Korea
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- The Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Egypt
- Kuwait
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East & Africa
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
Table Of Content
Methodology
FrequentlyAsked Questions
The global radiation dose-reduction system market is expected to grow due to increasing awareness of radiation safety, rising use of medical imaging, stringent regulatory guidelines, and advancements in dose-reduction technologies.
According to a study, the global radiation dose-reduction system market size was worth around USD 2.48 Billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 8.55 Billion by 2034.
The global radiation dose-reduction system market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 13.2% during the forecast period.
North America is expected to dominate the radiation dose-reduction system market over the forecast period.
Leading players in the global radiation dose-reduction system market include Bayer AG, Bracco Imaging SpA,Fujifilm Holdings Corporation,GE Healthcare, Medsquare, Novarad Corporation, PACShealth LLC, Koninklijke Philips N.V., Qaelum NV and Sectra AB, among others.
The report explores crucial aspects of the radiation dose-reduction system market, including a detailed discussion of existing growth factors and restraints, while also examining future growth opportunities and challenges that impact the market.
RelatedNews
HappyClients
Zion Market Research
Tel: +1 (302) 444-0166
USA/Canada Toll Free No.+1 (855) 465-4651
3rd Floor,
Mrunal Paradise, Opp Maharaja Hotel,
Pimple Gurav, Pune 411061,
Maharashtra, India
Phone No +91 7768 006 007, +91 7768 006 008
US OFFICE NO +1 (302) 444-0166
US/CAN TOLL FREE +1 (855) 465-4651
Email: sales@zionmarketresearch.com
We have secured system to process your transaction.
Our support available to help you 24 hours a day, five days a week.
Monday - Friday: 9AM - 6PM
Saturday - Sunday: Closed